Non-Fungible Token (NFT) is a unique new medium in the art world. It is touted as the evolution of art in the digital era.
The credit for the genesis of this art goes to Kevin McCoy, who created an NFT digital art called ‘Quantum’ in 2014. Since then, several digital artists have minted NFT art to unleash their imagination and earn money.
The NFT market generated $338 million in transaction volume in 2020. Furthermore, it is estimated that generative art could grow 1000 times in the next decade or more.
Have we piqued your interest in NFT art? Are you wondering what NFT art is? Here is all you need to know about it.
What is NFT art?
NFTs are the digital version of collectibles. They represent real-world things like artwork, music, memes, images, videos, GIFs, and avatars. They are encoded with blockchain technology that contains built-in authentication and acts as proof of ownership.
You can also say that NFTs are similar to digital assets like cryptocurrencies and bitcoins. However, both cryptocurrencies and bitcoins are fungible – you will get exactly the same thing if you exchange or trade them for an equal value.
NFTs are non-fungible, meaning that they are unique, and authentic and that they can’t be replaced with something else.
It is a piece of work that doesn’t exist anywhere. Something like the artwork Mona Lisa – there is only one original painting in the world. Another example would be a $10 bill signed by a celebrity – it can no longer be swapped with another $10 bill for an equivalent value.
Each NFT art piece has a digital signature, due to which it becomes impossible to trade it with another for an equal value.
How do NFTs work?
While cryptocurrencies are fungible (interchangeable with each other in value like cash), NFTs are definitively unique, and not mutually interchangeable.
As a result, NFTs create scarcity for infinitely available assets, with a certificate of authenticity to prove it. From music, trading cards, virtual land, jpegs, tweets, to even video game skins.
Let’s say a digital artist makes an image and posts it on his website. Hundreds of people download it, but nobody owns it in the real sense despite the artist being the original creator. However, if the same artist creates this image using blockchain and turns it into NFT, he becomes its owner. He gets the original credit for the image, no matter who downloads or duplicates it.
Blockchain makes it easy to verify the NFT art’s authenticity and ownership on a publicly accessible blockchain record or ledger. Blockchain ensures that their work is not duplicated, forged, or plagiarized.
What will NFTs do for creators?
NFTs have created an ownership economy in the digital art world. It has allowed the artists to get legal ownership of their content, monetize it, and build traction. NFTs have changed the relationship dynamic between artists or creators with brands and buyers.
Here are some ways artists are leveraging NFTs.
Digital art ownership
Before NFTs, artists hardly had any control over their content being reshared, reposted, or repurposed. It was challenging for them to establish ownership over their work.
However, NFTs have been a game-changer in this context. NFTs give the right to the artist to license, display, rent, or sell their artwork however and wherever they deem ideal. Artists get legal ownership for their NFTs.

When the artist lists the NFT on the blockchain, they get a private encryption key that proves the ownership. So even if the NFT links to the version of the work through someone else, the right to reproduce and distribute remains solely with the creator.
Income generation
NFT art market is thriving!
36-year-old NFT and portrait pop artist Blake Jamieson has earned $46k in just six weeks by selling his NFTs!
NFTs allow artists to stake claims over their artwork and earn money from it. They can earn rewards, royalties, and incentives in lieu of their content.
So, every time the artists’ NFT is rented, sold, or used in any other way, they are liable to get some monetary cut from it. Some artists even trade-in NFTs like stocks by buying and selling them profitably.
However, making money from NFTs takes time. The artists have to be consistent and patient in posting their work online. They also need to ensure that their work delivers value to the customers.
You can even launch an NFT startup or invest in one. These days, NFT startups are becoming a popular investment arena for venture capitalists, angel investors, and celebrities.
Read: How to sell NFT art?
Global audience
In a typical art trading scenario, the artwork is physical. It has to be transported from one place to another, whether bought or sold in person or virtually.
NFTs have bridged this gap. Since NFT artwork is entirely digital, there is no need for transportation. It is a huge saving and affordable deal for global buyers who love to invest in art from different countries.
So, NFTs help the artists reach a global audience and find new income generation opportunities.
How much are NFTs worth?
There is no definitive answer to this. NFTs can be worth a few hundred dollars to millions of dollars. NFT art prices depend on either of these two factors:
- Creators and their reputation
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP) of the artwork
NFT art creators Trevor Jones and Jose Delbo sold their artwork Genesis, a five-part collection depiction of Batman in pen, ink, and oil on canvas for $111,377 in 2020.
Krista Kim, the designer behind Mars House – the first digital home earned $500,000 for selling it.
Grimes, a musician, sold her digital art pieces for $6 million in 2021!
How to create NFT art?
NFT art creation is primarily a three-step process:
Step 1: Set up a Digital Wallet with Blockchain platform
Step 2: Upload the NFTs on Marketplaces
Step 3: Market the NFTs
For more on creating NFTs, read ‘How to Create NFT Art?’
Current Use Cases of NFTs
The most famous existing NFT use cases span virtual art collectables like CryptoPunks, Bored Apes Yacht Club, to even domain name NFTs like apple.eth. As well as historic NBA moments that demonstrate memorable plays sold to fans. For instance, LeBron James’s dunk sold for $400k on NBA Topshots.
Pak’s ‘The Merge’
Pak’s Merge recently dethroned Beeple’s First 5000 Days to become the most expensive NFT ever sold. This occurred on December 2, 2021, as almost 30,000 collectors pitched together to make the $91.8m purchase.
This NFT Collectable was sold in an open edition as buyers were allowed to purchase any number of tokens from a unit price of US$575. This price impressively increased by $25 every six hours. By the end, the tokens sold for a total of US$91.8 million.
CryptoPunks
Cryptopunks constitute unique pixel art characters generated on the Ethereum blockchain by Larva Labs’s software. Though it initially started as an experiment to create an app or game, Larva Labs ended up with 10,000 Cryptopunks algorithmically generated with code in June 2017.

This collection of 8-bit-style pixel art images comprises 10,000 avatars, with randomly generated features that distinguish each piece. Despite being initially offered free of charge when launched, they were later sold for $1 to $30 in 2017. Later on, they sold for an average price of $54,000, with some even being worth thousands of dollars, and even millions.
Bored Ape Yacht Club
This unique set of collectables takes inspiration from NFT projects like CryptoPunks. However, the Bored Ape Yacht Club comprises ‘bored looking’ digital Apes with different clothing and backgrounds.
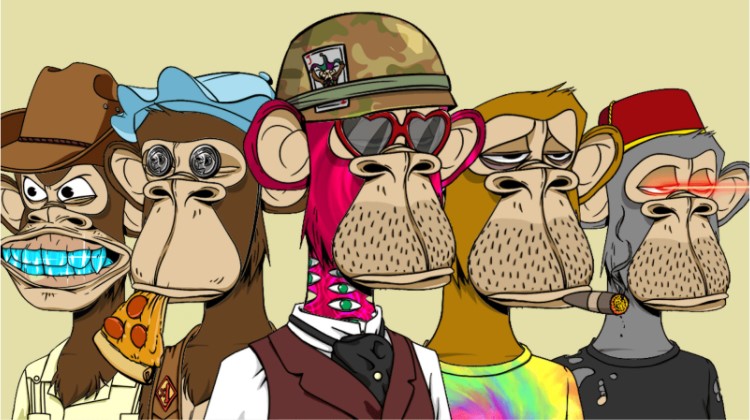

Created by Yuga Labs’ four pseudonymous founders, this NFT collectables project was inspired by the “aping in” term to present individuals who purchase new crypto, or NFTs without considering the inherent risks involved.
Later on, the Yuga Labs added two follow up collectables, Bored Ape Kennel Club and Mutant Ape Yacht Club. Bored Ape members (owners) are typically given the Kennel Dog NFT for free of charge (apart from the gas fee).
On 30th April 2021, 10,000 apes were sold for 0.08 ETH (approximately US$200). Currently, the most expensive Bored Ape, Ape 6618, was sold for US$3.4 million.
Art Blocks
This is a unique use case of NFTs that involves generative art. As a generative art platform, Art Block allows collectors to mint unique tokens, without knowing what they will receive ahead of time. Essentially, the digital artist writes a tailored code that is plugged into the platform. This code then generates different randomized combinations of variables.

The creator of Art Blocks, Erick Snowfro, had the idea when claiming CryptoPunks in 2017. He reasoned that it was unfair that he was limited to claiming a bunch of zombies. Consequently, over the following years, he sold over 20 zombies to fund his Art Blocks project. Currently, the most expensive Art Block piece, Ringers #879, sold for $5.8m.
What are some potential NFT future use cases?
Music NFTs: NFTs have the potential to disrupt traditional music business models for artists and record labels. The existing 50/50 model involves 50% going to the musician, with the rest shared amongst the label, agents, lawyers, and distributors.
NFTs could provide an avenue for artists to self-publish and cut out agents and distributors, essentially leading to the democratization of the music industry.
NFT Gaming: NFTs are slowly being adopted to create non-duplicable in-game items. Therefore, enabling gamers to access an unprecedented form of ownership never seen before.
While a relatively new concept, NFT gaming is quickly gaining popularity. The Binance NFT Initial Game Offering (IGO) is a testament to this. This new gaming arm exceeded $16 million in trading volume in less than two weeks, with every IGO’s NFT collection completely sold out.
Furthermore, NFT adoption is extending to gamified virtual spaces like the Metaverse that could disrupt the traditional social network paradigm. Already closely interconnected, especially in blockchain gaming, NFT ownership could be the key that opens up endless opportunities in the emerging metaverses. For example, facilitating identity, user interaction, social experiences, and even transactions in the Metaverse. Real-world asset NFTs: NFTs linked to real-world assets could digitize how we prove ownership. For instance, the real estate world, which typically entails physical property deeds, could later employ tokenized digital assets of deeds. Thus, moving highly illiquid items (like houses or land) onto the blockchain.
Generative Art products: Psychedelic art-based designs are gaining popularity in the merchandising world. Generative art provides excellent inspiration for various products like wall art, home decor, apparel, furniture and interiors, etc. Check out some unique psychedelic art products at TrippyMojo.
How to sell NFT art?
NFT artists can sell their artwork on various platforms available such as Open Sea, Rarible, Mintable or Zora. There are also platforms such as Nifty Gateway that allow you to submit your artwork for curation. You can list your work here at a fixed price or you can run an auction to sell your artwork.
Once you’ve sold a piece, the marketplace will take care of the transaction. It will transfer the money from the buyer to the seller after deducting the listing fee and other transaction expenses. Your funds will be transferred directly into your digital crypto wallet.
How to invest in NFT art?
If you want to buy NFT digital art, you will need to open a crypto wallet account on a marketplace to purchase the artwork. There are some key factors to look out for when considering investing in an NFT art piece. The goal of investing is to choose a work that will increase in value and add value to give you a profit.
Good NFT projects will have a clear marketing roadmap that will show their future plans for the project. This will help you gauge if the project will be successful and give you high returns. The projects will also vary with benefits that members get such as access to whitelists, varied licensing rights, and community involvement. Select one that has benefits you will enjoy and will boost the profitability of the NFT.
However, if you are an amateur or a newbie to NFT marketplaces, it is advisable to study the market trends and spend some time researching NFTs to avoid making a wrong purchase.
NFT art examples and creators
Creators worldwide have adopted NFT art for its popularity and have monetized it to their advantage. Let’s take a look at some of these creators and their creations.
- Kevin McCoy – Quantum
- Mike Winkelmann (Beeple) – Everydays: The First 5000 Days
- Trevor Jones – The Bitcoin Angel
- Fewocious – The Everlasting Beautiful
- Trevor Andrew – Gucci Ghost
- Pak – Metarift
- Krista Kims – Mars House
- Blake Kathryn – Seasons
- Mad Dog Jones – Boardwalk
- Xcopy – Death Dip
Conclusion
The use cases for NFTs are fast expanding, heralding a new era of the digital world. The arrival of metaverses like Facebook’s launch of Meta could see NFT-based augmented experiences serving as pillars for next-generation social networks.
NFT calls for knowledge of fairly complex computers and digital technology for artists. If you can crack the code, you can strike gold in NFT art with patience and consistency. As far as investing in NFT art is concerned, buyers should understand the market and associated risks.
Some experts even think that NFT is a bubble that may burst soon. However, it is too early to say this because NFT is still in the nascent stage. At present, there is no doubt that it has revolutionized the art world.



